Aufgaben:Aufgabe 2.4: 2D-Übertragungsfunktion: Unterschied zwischen den Versionen
K (Guenter verschob die Seite Aufgabe 2.4: 2D-Übertragungsfunktion aus 2D-Impulsantwort nach Aufgabe 2.4: 2D-Übertragungsfunktion) |
|||
| Zeile 2: | Zeile 2: | ||
{{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile Kommunikation/Mehrwegeempfang beim Mobilfunk}} | {{quiz-Header|Buchseite=Mobile Kommunikation/Mehrwegeempfang beim Mobilfunk}} | ||
| − | [[Datei:P_ID2161__Mob_A_2_4.png|right|frame|2D–Impulsantwort $|h(\tau, t)|$]] | + | [[Datei:P_ID2161__Mob_A_2_4.png|right|frame|2D–Impulsantwort $|h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t)|$]] |
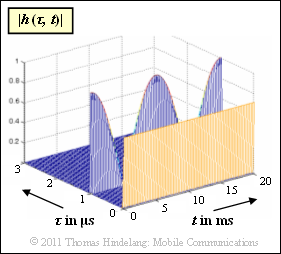
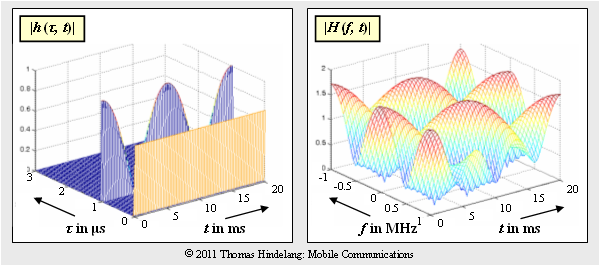
| − | Dargestellt ist die zweidimensionale Impulsantwort $h(\tau, t)$ eines Mobilfunksystems in Betragsdarstellung. Es ist zu erkennen, dass die 2D–Impulsantwort nur für die Verzögerungszeiten $\tau = 0$ und $\tau = 1 \ \rm \mu s$ Anteile besitzt. Zu diesen Zeitpunkten gilt: | + | Dargestellt ist die zweidimensionale Impulsantwort $h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t)$ eines Mobilfunksystems in Betragsdarstellung. Es ist zu erkennen, dass die 2D–Impulsantwort nur für die Verzögerungszeiten $\tau = 0$ und $\tau = 1 \ \rm \mu s$ Anteile besitzt. Zu diesen Zeitpunkten gilt: |
:$$h(\tau = 0\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} = {\rm const.}$$ | :$$h(\tau = 0\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} = {\rm const.}$$ | ||
:$$h(\tau = 1\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \cos(2\pi \cdot {t}/{ T_0})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | :$$h(\tau = 1\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \cos(2\pi \cdot {t}/{ T_0})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| − | Für alle anderen $\tau$–Werte ist $h(\tau, t) | + | Für alle anderen $\tau$–Werte ist $h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t) \equiv 0$. |
| − | Gesucht ist die zweidimensionale Übertragungsfunktion $H(f, t)$ als die Fouriertransformierte von $h(\tau, t)$ hinsichtlich der Verzögerungszeit $\tau$: | + | Gesucht ist die zweidimensionale Übertragungsfunktion $H(f, \hspace{0.05cm} t)$ als die Fouriertransformierte von $h(\tau, t)$ hinsichtlich der Verzögerungszeit $\tau$: |
:$$H(f,\hspace{0.05cm} t) | :$$H(f,\hspace{0.05cm} t) | ||
\hspace{0.2cm} \stackrel {f,\hspace{0.05cm}\tau}{\bullet\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\circ} \hspace{0.2cm} h(\tau,\hspace{0.05cm}t) | \hspace{0.2cm} \stackrel {f,\hspace{0.05cm}\tau}{\bullet\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\circ} \hspace{0.2cm} h(\tau,\hspace{0.05cm}t) | ||
\hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | \hspace{0.05cm}.$$ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
''Hinweise:'' | ''Hinweise:'' | ||
* Die Aufgabe gehört zum Kapitel [[Mobile_Kommunikation/Mehrwegeempfang_beim_Mobilfunk| Mehrwegeempfang beim Mobilfunk]]. | * Die Aufgabe gehört zum Kapitel [[Mobile_Kommunikation/Mehrwegeempfang_beim_Mobilfunk| Mehrwegeempfang beim Mobilfunk]]. | ||
| − | * Eine ähnliche Problematik wird in der [[Aufgaben:2.5_Scatter-Funktion| Aufgabe | + | * Eine ähnliche Problematik wird in der [[Aufgaben:2.5_Scatter-Funktion| Aufgabe 2.5]] behandelt, allerdings mit veränderter Nomenklatur. |
* Sollte die Eingabe des Zahlenwertes „0” erforderlich sein, so geben Sie bitte „0.” ein. | * Sollte die Eingabe des Zahlenwertes „0” erforderlich sein, so geben Sie bitte „0.” ein. | ||
| Zeile 24: | Zeile 26: | ||
===Fragebogen=== | ===Fragebogen=== | ||
<quiz display=simple> | <quiz display=simple> | ||
| − | {Wie groß ist die Periodendauer $T_0$ der Funktion $h(\tau = 1 \ {\rm \mu s}, t)$? Beachten Sie, dass in der Grafik der Betrag $|h(\tau, t)|$ dargestellt ist. | + | {Wie groß ist die Periodendauer $T_0$ der Funktion $h(\tau = 1 \ {\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm} t)$? Beachten Sie, dass in der Grafik der Betrag $|h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t)|$ dargestellt ist. |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$T_0 \ = \ ${ 20 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | $T_0 \ = \ ${ 20 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | ||
| − | {Zu welchen Zeiten $t_1$ (zwischen $0$ und $10 \ \rm ms$) und $t_2$ (zwischen $10 \ \rm ms$ und $20 \ \rm ms$) ist $H(f, t)$ bezüglich $f$ konstant? | + | {Zu welchen Zeiten $t_1$ (zwischen $0$ und $10 \ \rm ms$) und $t_2$ (zwischen $10 \ \rm ms$ und $20 \ \rm ms$) ist $H(f, \hspace{0.05cm}t)$ bezüglich $f$ konstant? |
|type="{}"} | |type="{}"} | ||
$t_1 \ = \ ${ 5 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | $t_1 \ = \ ${ 5 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | ||
$t_2 \ = \ ${ 15 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | $t_2 \ = \ ${ 15 3% } $\ \rm ms$ | ||
| − | {Berechnen Sie $H_0(f) = H(f, t = 0)$. Welche Aussagen sind zutreffend? | + | {Berechnen Sie $H_0(f) = H(f, \hspace{0.05cm}t = 0)$. Welche Aussagen sind zutreffend? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + Es gilt $H_0(f) = H_0(f + i \cdot 1 \ {\rm MHz}), i = ±1, ±2, \ ...$ | + | + Es gilt $H_0(f) = H_0(f + i \cdot 1 \ {\rm MHz}), i = ±1, ±2, \ \text{...}$ |
+ Es gilt näherungsweise $0.293 ≤ |H_0(f)| ≤ 1.707$. | + Es gilt näherungsweise $0.293 ≤ |H_0(f)| ≤ 1.707$. | ||
+ $|H_0(f)|$ hat bei $f = 0$ ein Maximum. | + $|H_0(f)|$ hat bei $f = 0$ ein Maximum. | ||
| − | {Berechnen Sie $H_{10}(f) = H(f, t = 10 \ \rm ms)$. Welche Aussagen sind zutreffend? | + | {Berechnen Sie $H_{10}(f) = H(f, \hspace{0.05cm}t = 10 \ \rm ms)$. Welche Aussagen sind zutreffend? |
|type="[]"} | |type="[]"} | ||
| − | + Es gilt $H_{10}(f) = H_{10}(f + i \cdot 1 \ \rm MHz), i = ±1, ±2, \ ...$ | + | + Es gilt $H_{10}(f) = H_{10}(f + i \cdot 1 \ \rm MHz), i = ±1, ±2, \ \text{...}$ |
+ Es gilt näherungsweise $0.293 ≤ H_{10}(f) ≤ 1.707$. | + Es gilt näherungsweise $0.293 ≤ H_{10}(f) ≤ 1.707$. | ||
- $|H_{10}(f)|$ hat bei $f = 0$ ein Maximum. | - $|H_{10}(f)|$ hat bei $f = 0$ ein Maximum. | ||
Version vom 5. Dezember 2017, 16:46 Uhr
Dargestellt ist die zweidimensionale Impulsantwort $h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t)$ eines Mobilfunksystems in Betragsdarstellung. Es ist zu erkennen, dass die 2D–Impulsantwort nur für die Verzögerungszeiten $\tau = 0$ und $\tau = 1 \ \rm \mu s$ Anteile besitzt. Zu diesen Zeitpunkten gilt:
- $$h(\tau = 0\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} = {\rm const.}$$
- $$h(\tau = 1\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \cos(2\pi \cdot {t}/{ T_0})\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Für alle anderen $\tau$–Werte ist $h(\tau, \hspace{0.05cm}t) \equiv 0$.
Gesucht ist die zweidimensionale Übertragungsfunktion $H(f, \hspace{0.05cm} t)$ als die Fouriertransformierte von $h(\tau, t)$ hinsichtlich der Verzögerungszeit $\tau$:
- $$H(f,\hspace{0.05cm} t) \hspace{0.2cm} \stackrel {f,\hspace{0.05cm}\tau}{\bullet\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\!-\!\!\circ} \hspace{0.2cm} h(\tau,\hspace{0.05cm}t) \hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Hinweise:
- Die Aufgabe gehört zum Kapitel Mehrwegeempfang beim Mobilfunk.
- Eine ähnliche Problematik wird in der Aufgabe 2.5 behandelt, allerdings mit veränderter Nomenklatur.
- Sollte die Eingabe des Zahlenwertes „0” erforderlich sein, so geben Sie bitte „0.” ein.
Fragebogen
Musterlösung
(2) Zum Zeitpunkt $t_1 \ \underline {= 5 \ \rm ms}$ ist $h(\tau = 1 \ {\rm \mu s}, t_1) = 0$. Dementsprechend gilt
- $$h(\tau = 1\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t_1) = \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} \cdot \delta(\tau)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H(f,\hspace{0.05cm}t_1) = \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} = {\rm const.}$$
Ebenso gilt für $t_2 \ \underline {= 15 \ \rm ms}$:
- $$h(\tau = 1\,{\rm \mu s},\hspace{0.05cm}t_2) = \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} \cdot \delta(\tau)\hspace{0.3cm}\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} H(f,\hspace{0.05cm}t_2) = \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} = {\rm const.}$$
(3) Zum Zeitpunkt $t = 0$ lautet die Impulsantwort mit $\tau_1 = 1 \ \rm \mu s$:
- $$h(\tau,\hspace{0.05cm}t = 0) = \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} \cdot \delta(\tau)+ \delta(\tau - \tau_1)\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Die Fouriertransformation führt zum Ergebnis:
- $$H_0(f) = H(f,\hspace{0.05cm}t = 0) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} + 1 \cdot {\rm exp}(- {\rm j}\cdot 2 \pi f \tau_1)=$$
- $$\hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} + \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1)- {\rm j}\cdot \sin( 2 \pi f \tau_1)$$
- $$\Rightarrow \hspace{0.3cm} |H_0(f)| \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sqrt { \left [ {1}/{ \sqrt{2}} + \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1) \right ]^2 + \left [\sin( 2 \pi f \tau_1)\right ]^2}=$$
- $$\hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sqrt { 0.5 + 1 + {2}/{ \sqrt{2}} \cdot \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1)} = \sqrt { 1.5 + { \sqrt{2}} \cdot \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Daraus folgt:
- $H_0(f)$ ist periodisch mit $1/\tau_1 = 1 \ \rm MHz$.
- Für den Maximalwert bzw. Minimalwert gilt:
- $${\rm Max}\, \left [ \, |H_0(f)|\, \right ] \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sqrt { 1.5 + { \sqrt{2}} } \approx 1.707 \hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $${\rm Min}\, \left [ \, |H_0(f)|\, \right ] \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sqrt { 1.5 - { \sqrt{2}} } \approx 0.293 \hspace{0.05cm}. $$
- Bei $f = 0$ hat $|H_0(f)$ ein Maximum.
Richtig sind demzufolge alle drei Lösungsvorschläge.
(4) Für den Zeitpunkt $t = 10 \ \rm ms$ gelten folgende Gleichungen:
- $$h(\tau,\hspace{0.05cm}t = 10\,{\rm ms}) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} \cdot \delta(\tau)- \delta(\tau - \tau_1)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$H_{10}(f) = H(f,\hspace{0.05cm}t = 10\,{\rm ms}) \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \frac{1}{ \sqrt{2}} - \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1)+ {\rm j}\cdot \sin( 2 \pi f \tau_1)\hspace{0.05cm},$$
- $$ |H_{10}(f)| \hspace{-0.1cm} \ = \ \hspace{-0.1cm} \sqrt { 1.5 - { \sqrt{2}} \cdot \cos( 2 \pi f \tau_1)}\hspace{0.05cm}.$$
Die Frequenzperiode ändert sich gegenüber $t = 0$ nicht. Der Maximalwert ist weiterhin $1.707$ und auch der Minimalwer $0.293$ ändert sich nicht gegenüber der Teilaufgabe (3). Bei $f = 0$ tritt nun allerdings ein Minimum und kein Maximum auf ⇒ Richtig sind die Lösungsvorschläge 1 und 2.
Die rechte Grafik zeigt den Betrag $|H(f, t)|$ der zweidimensionalen Übertragungsfunktion.